Describe the Nucleotide Pairings Used by Mrna to Transcribe Information
The amino acids used for protein synthesis are first attached to a family of tRNA molecules each of which recognizes by complementary base -pair interactions particular sets of three nucleotides in the mRNA. What is the function of the polyA tail.
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
During translation the information that is.

. - mRNA contains a nitrogenous base a sugar and a phosphate group like. Messenger RNA mRNA. Much like how RNA is built from many nucleotides a protein is formed from many amino acids.
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes perform fundamentally the same process of transcription with the important difference of the membrane-bound nucleus in eukaryotes. Look at the figure on the bottom of page 4 It makes sense to use the word translation when referring to protein synthesis because the information on the mRNA codons already exists in the cell. During protein synthesis an organelle called a ribosome moves along the mRNA reads its base sequence.
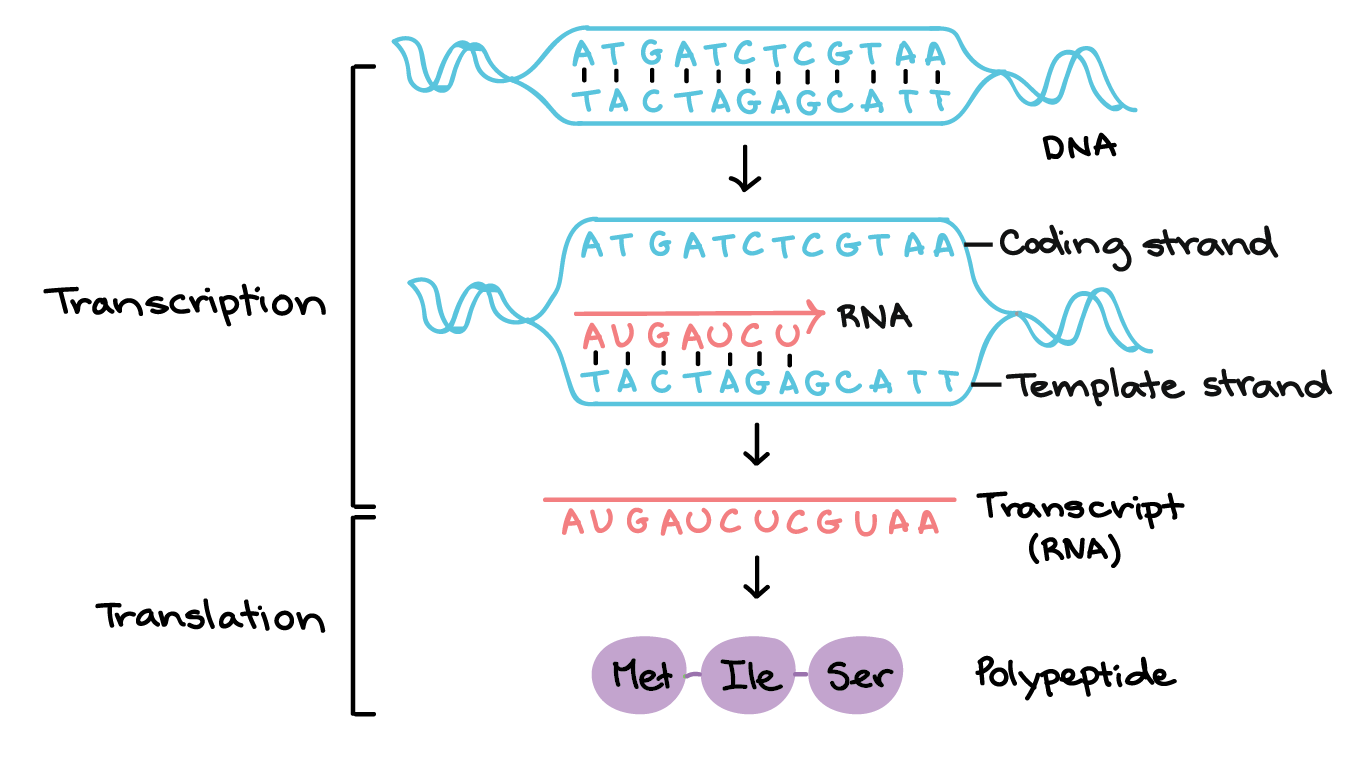
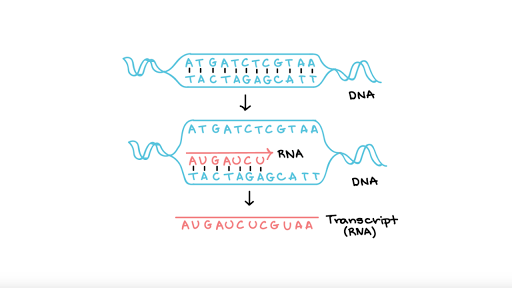
A nitrogenous base a pentose five-carbon sugar called ribose. Define mRNA and its purpose. One strand of the molecule is the template strand and one is called the coding strand.
2mRNA nucleotides join with exposed DNA bases and form a molecule of mRNA 3The mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus 4A ribosome attaches to the mRNA molecule 5tRNA molecules bring specific amino acids to the mRNA molecule 6Peptide bonds form between the amino acids. The bases will always pair A with T and C with G. Only one strand of DNA is copied during the process of transcription known as the template strand and the RNA formed is called the mRNA.
Describe the structure and potential products of a gene polypeptide rRNA tRNA mRNA and the types of proteins required for transcription RNA polymerases transcription factors etc. Messenger RNA mRNA is a single-stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to one of the DNA strands of a gene. Which RNA nucleotide can pair with the ThymineTat the beginning of the strand.
A nitrogenous base a pentose sugar called ribose and a phosphate orginations. Explain where transcription occurs in the cell. - Guanine G pairs with cytosine C in mRNA and DNA.
MRNA is transcribed 2. The genetic information flows from DNA to protein and this flow of information takes place in a sequential process of transcription and translation. There are three building blocks on every nucleotide.
Once an mRNA molecule is complete that molecule can go on to play a key role in the process known as translation. The translation of the nucleotide sequence of an mRNA molecule into protein takes place in the cytoplasm on a large ribonucleoprotein assembly called a ribosome. Describe the flow of information through cells the central dogma and the cell components that participate.
The mRNA is an RNA version of the gene that leaves the cell nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm where proteins are made. RNA processing is the term collectively used to describe the sequence of events through which the primary transcript from a gene acquires its mature form. T thymine is used in DNA so A pairs with T in DNA Transcription.
The polyA tail provides a means of producing more than one mature mRNA transcript because the segment that is removed and the addition of the polyA tail can be done at different sites. What Monomers Are Used To Make The Molecule Made In Transcription. From DNA to mRNA.
To do this the DNA is read or. RNA polymerase is the enzyme which carries out transcription 4. It will pair the appropriate nucleutides with their partners on the template strand of DNA using ACG and U U replaces T in RNA Here is a video.
The 3 end of the messenger RNA mRNA is modified by the addition of a long string of adenosines in a process tightly linked to transcription termination. - The nucleotide matching in RNA follows a base pairing rule like the base pairing rule observed in the DNA double helix. In contrast to DNA in the field of RNA monomers called nucleotides make up the proteins.
When the RNA polymerase transcribes the DNA it reads only the template strand. With the genes bound in the nucleus transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell and the mRNA transcript must be transported to the cytoplasm. Translation is the process that takes the information passed from DNA as messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds.
The rRNA is associated with specific proteins to form ribosomes. Describe the goal of mRNA translation and identify the cellular structure that performs. Compare the similarities and differences between DNA and mRNA.
The specific sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA molecule provides the code for the production of a protein with a specific sequence of amino acids. MRNA directs the synthesis of proteins through a process known as translationmRNA directs which amino acids have to be added to the polypeptide chain and it does this by directing the tRNAEach mRNA has a set of three nucleotides known as codon that is recognized by an anticodon on the tRNAThe codon and anticodon match each other through base pairing rules. The mRNA carries the message of transcript DNA codes of polypeptides from the nucleus to the ribosomes.
It is essentially a translation from one code nucleotide sequence to. Transcribe the information in DNA to mRNA. Removal of terminal segments of the mRNA and placing numerous adenin-containing ribonucleotides at the tail end of the mRNA.
Translation is the process where the information carried in mRNA molecules is used to create proteins. Promoter RNA-coding region terminator. The tRNA carries specific amino acids to the ribosome aiding the translation.
Describe the goal of DNA transcription and identify the enzyme primarily involved in this process. Explain why it makes sense to use the word translation to describe protein synthesis and why it would not make sense to use the word translation to describe mRNA synthesis. Used in transcription to produce the mRNA.
Look at the figure on the bottom of page 4 Since it only needs to be translated from one type to another form of nucleotide to an amino acid and the information on the mRNA is already there in the cell. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes the second function of DNA the first was replication is to provide the information needed to construct the proteins necessary so that the cell can perform all of its functions. T thymine is replaced by U uracil in RNA so A in DNA pairs with U in mRNA.
Explain why it makes sense to use the word translation to describe protein synthesis and why it would not make sense to use the word translation to describe mRNA synthesis. Nucleotide sequence 20-200 bp long initial binding site of RNA polymerase and transcription initiation factors recognized by RNA pol.

Solved Describe The Nucleotide Pairings Used By Mrna To Chegg Com
Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy

Comments
Post a Comment